Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a comprehensive software solution that integrates core business processes and functions into a unified system, allowing organizations to manage and streamline their operations more effectively. ERP systems typically cover a wide range of business activities, including finance, accounting, human resources, supply chain management, manufacturing, sales, and customer relationship management (CRM). Here's an overview of how ERP works and its key components:
1. **Integration**: ERP systems integrate data and processes from various departments and functions across an organization into a single centralized database. This integration eliminates data silos and enables real-time visibility and collaboration across different business units, leading to improved communication, efficiency, and decision-making.
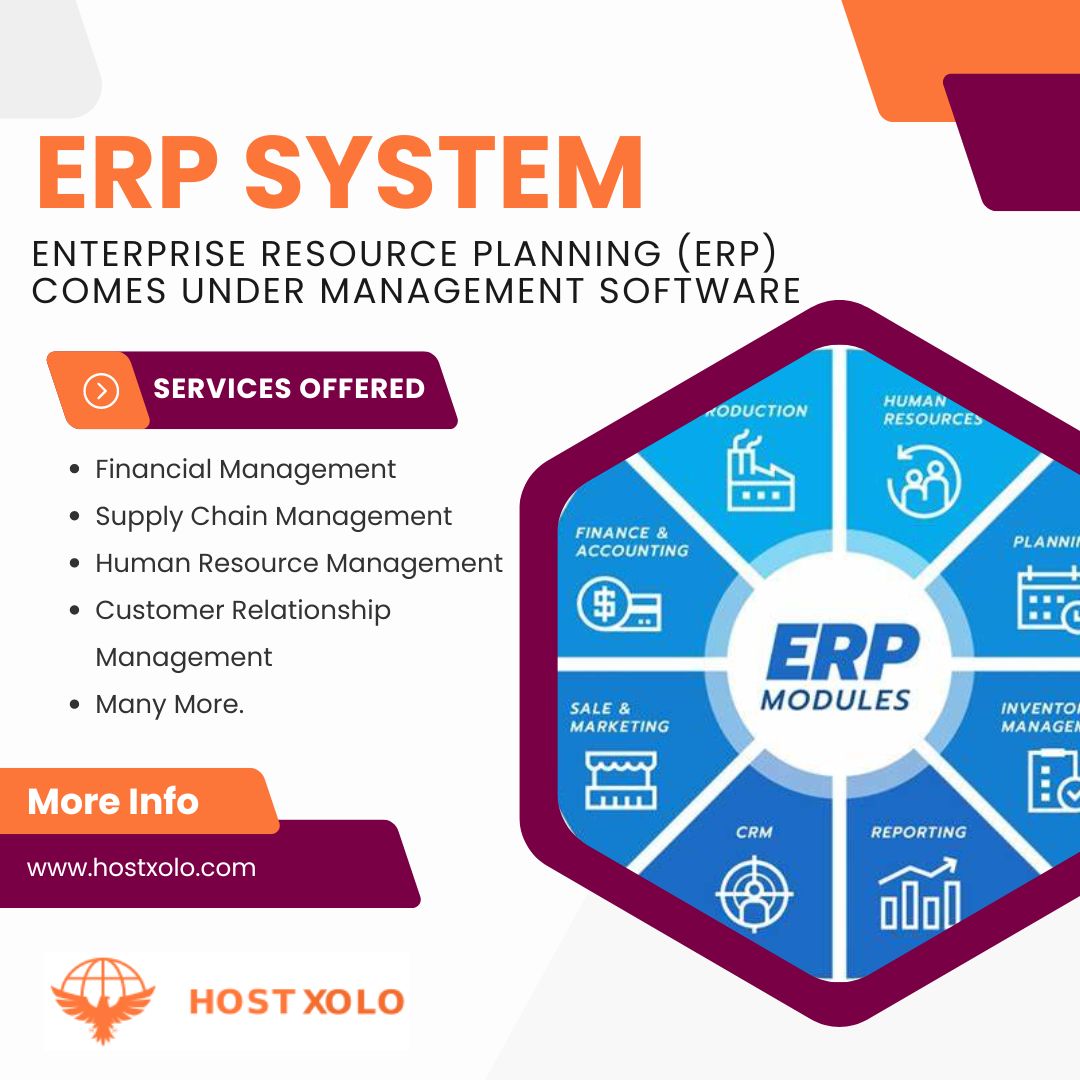
2. **Modules**: ERP systems consist of different modules or applications that correspond to specific business functions or departments. Each module typically includes a set of features and functionalities tailored to the needs of that particular area. Common ERP modules include:
- Finance and Accounting: Manages financial transactions, budgeting, invoicing, accounts payable/receivable, and financial reporting.
- Human Resources (HR): Handles employee data, payroll processing, benefits administration, recruitment, training, and performance management.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): Oversees procurement, inventory management, supplier relationship management, demand forecasting, and logistics.
- Manufacturing: Manages production planning, scheduling, quality control, materials management, and shop floor operations.
- Sales and Distribution: Tracks sales orders, customer inquiries, pricing, order fulfillment, and delivery scheduling.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Manages customer interactions, sales pipelines, marketing campaigns, lead generation, and customer service.
3. **Data Analytics**: ERP systems provide advanced reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing organizations to analyze key performance indicators (KPIs), trends, and insights across different areas of their business. These analytics enable data-driven decision-making, strategic planning, and continuous improvement initiatives.
4. **Customization and Scalability**: ERP systems are highly customizable to accommodate the unique needs and workflows of different industries and organizations. They can be configured to support specific business processes, compliance requirements, and industry standards. Additionally, ERP systems are scalable, allowing organizations to adapt and expand their ERP implementation as their business grows or evolves.
5. **Cloud-Based ERP**: In recent years, many ERP vendors have transitioned to offering cloud-based ERP solutions, which are hosted and accessed over the internet. Cloud ERP offers several benefits, including lower upfront costs, faster implementation, automatic updates, remote accessibility, and scalability.
Overall, ERP systems play a critical role in helping organizations streamline their operations, improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance visibility and control, and drive growth and innovation. By integrating and automating core business processes, ERP enables organizations to operate more competitively in today's dynamic and interconnected business environment.